Our Diamonds
Love persists when perfection exists
There is no other gemstone quite like a diamond. It is found in the most remote places on earth, and the fact that it forms at all is something of a miracle. It takes about one ton of rock to recover less than half a carat of rough.
This makes diamonds one of the rarest and most desired gemstones in the world. A diamond is a testament of endurance and strength – and not surprisingly, the ultimate symbol of love.
Color: Colorless beauty

Although many people think of gem quality diamonds as colorless, truly colorless diamonds are actually very rare. Most diamonds used in jewelry are nearly colorless with tints of yellow or brown. Color grades are determined by comparing each diamond to a master set. Each letter grade represents a range of color and is a measure of how noticeable a color is.
The GIA Color Scale extends from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
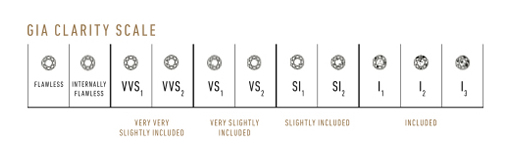
Clarity: Clearly Superb
Because diamonds form under tremendous heat and pressure, it is extremely rare to find a diamond that lacks any internal and external characteristics. These characteristics are a by-product of its formation and help gemologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and simulants, and identify individual stones.
The GIA Clarity Scale includes eleven clarity grades ranging from Flawless to I3.
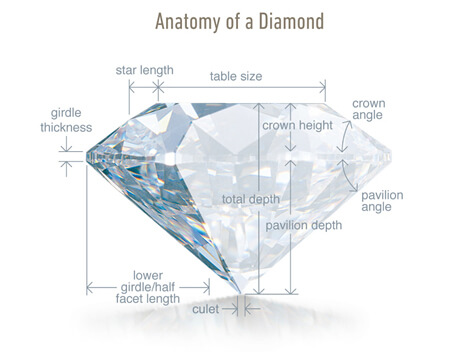
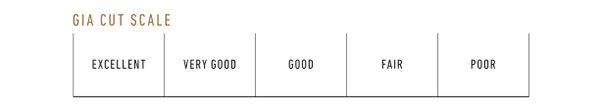
Cut: Shear Brilliance and Life
A polished diamond’s beauty lies in its complex relationship with light. The magnificent display you see is made up of three attributes: Brightness is the combination of all white light reflecting from the surface and interior of a diamond. Fire describes the “flares” of color emitted from a diamond. Scintillation describes the pattern of light and dark areas and the sparkle you see when the diamond, the light, or the observer moves. A diamond’s proportions affect its light performance, which in turn affects its beauty and overall appeal. Diamonds with fine proportions, symmetry, and polish optimize their interaction with light, and have increased brightness, fire, and scintillation. GIA assesses these factors for standard round brilliant diamonds in the D-to-Z color range.
The GIA Cut Scale ranges from Excellent to Poor.
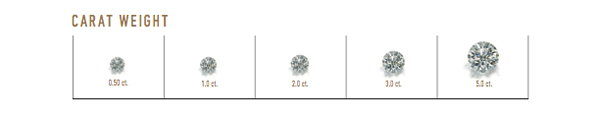
Carat Weight: What's the point?
For diamonds under one carat, each carat is divided into 100 points – similar to pennies in a dollar. 0.75 ct. = 75 points, 1/2 ct. = 50 points.
One carat equals 200 milligrams in weight.